Bag of Visual Words
撰写于 2020-11-05 修改于 2021-07-07 views
Bag of Visual Words
What is an bag of visual words?
Bag of visual words refers to techniques that allows us to compactly describe images and to perform similarities queries. So given a database of images the bag of visual words approach can be used to efficiently find subsets of images that look similar either among each other or with respect to a given query image. So how does that work? So the bag of visual words uses a set of image features as so-called visual words. Then it describes the images by simply counting how often individual visual words appear in an image. So here’s an example of a regular image what we can do we can extract part locations at which e compute feature descriptors such as sift features and are shown over here. So let us illustrate the different visual words now with colored boxes, each color box means there’s an occurrence of one visual word. Of course this is a very simplified illustration here just showing a few visual words.


So in the end each image is reduced to visual words and the actual pixel values do not matter anymore. So in bag of words, each image becomes in histogram simply counting the occurrences of the visual words within this image. So the x axis of the histogram defines the visual words while the y axis of the histogram how often the individual visual words appear in the image.
A visual word can be a single feature, most approaches however will use the mean feature descriptor computed from several similar descriptors at the visual _. That means we are grouping visual features together into one word in this grouping is typically computed using a clustering algorithm such as k-means. The visual words that result from clustering are called the dictionary. And they are lists of visual words and they define the x axis of all our histograms. So each image in our database is turned into such histogram so that need to store M histograms instead of M images in our database. And all comparisons are reduced to computing the similarity between histograms. And we are not considering the actual images anymore.
And there is however an issue with this approach because in practice some visual words are good for performing such a comparisons while others are less expressive. So for example if you have a word which occurs in every image will not be a great support for making comparisons. So we can fix this issue by computing a weight for each visual word depending on the expected information it is going to convey. So important visual words are ranked higher and others are lower. This is done using the so-called TF-IDT, tf-idf stands for term frequency inverse document frequency.

The first term in this equation is the relative occurrence of a word in image such as our histogram just normalized to 1, this term then multiplied with the logarithm of the inverse percentage of images in our database contain the word at all. This will bring the importance of the words that appear in every image down to 0. Other more rarely occurring words are enhanced. So tf-idf will relate each bin of each histogram individually and that expressive visual word will be enhanced. This tf-idf computations on all histogram in our database and now we are ready for comparing images in the database either among each other of respect to a query image.
So let’s consider more example with 4 images shown over here.
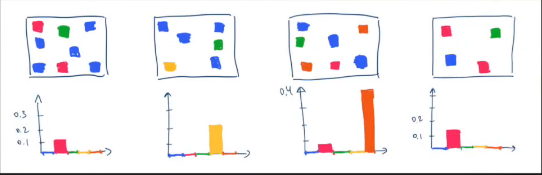
And this example number 0 and number 3 are similar to each other. By looking into the cost matrix of the histograms, we can see that each histogram compared with itself has a distance of 0 and all other comparisons lead to higher values actually not all of them. We also see the image number 0 and number 3 have a distance of zero which means they have the same distribution of related features and such they are considered to be similar or maybe identical.
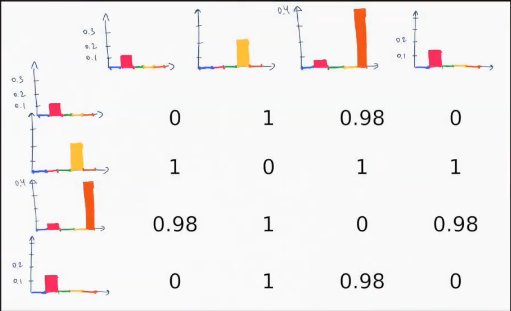
In the bag of words model we typically compare these histograms using the cosine distance which takes value between 0 and 1. So in order to find the N most similar images in database given _ images we will return the N images which have the smallest cosine distance. So that’s basically of it, that’s how we defined similar images. So the bag of words approach frequently used in computer vision for finding similar images. Also in robotics it’s used for performing place recognition tasks or for finding loop closure candidates in the context of the slam program. If you wanna to investigate the bag of visual words approach further, I suggest you to visit the jupiter notebook that was created by ovysotska and which is available on github. It’s a great point for understanding the effect of tf-idf and also the distance functions.